Coffee is one of the most popular potables encyclopedically, cherished for its rich flavor and amping goods. Beyond its capability to kickstart your morning, regular coffee consumption offers several health benefits, particularly in reducing the threat of type 2 diabetes. Then is a detailed look at how coffee affects our health, glucose situations, and the stylish practices for optimizing its benefits.
Table of Contents
ToggleHealth Benefits of Coffee
Regular consumption of coffee has been associated with multitudinous health benefits. One significant advantage is its potential to reduce the threat of type 2 diabetes. This effect is incompletely due to coffee’s capability to ameliorate liver fat burning and reduce stress in pancreatic beta cells. The liver plays a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar situations, and by enhancing its function, coffee helps maintain healthier glucose situations. also, lower stress on pancreatic beta cells translates to more insulin production and regulation, further lowering diabetes threat.
Glucose and Stress Response
While coffee can be salutary, it’s essential to understand its impact on glucose and stress response. Drinking black coffee can cause a slight increase in glucose levels for some individuals. This is due to caffeine driving the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which in turn cause glucose to be released into the bloodstream. This response is generally mild but can vary depending on individual perceptivity to caffeine.
Optimal Coffee Timing
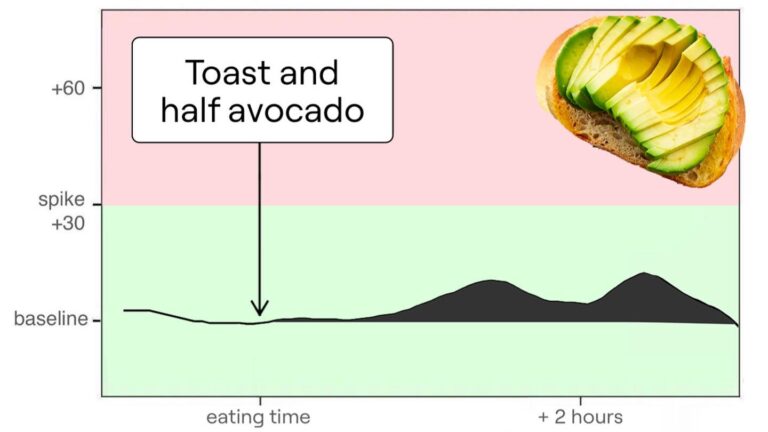
The timing of coffee consumption can significantly impact its impact on glucose situations. Research suggests that drinking coffee after breakfast, especially after a night of poor sleep, can reduce glucose levels by over 50 percent compared to having it before breakfast. This is because food in the stomach helps to moderate the immersion of caffeine, leading to a more balanced glucose response.
Impact of Complements
What you add to your coffee can also affect your blood sugar situations. Adding sugar to coffee can cause a significant increase in glucose levels, which can be mischievous, especially for those covering their blood sugar. To enjoy coffee without the shaft, consider druthers like Stevia, cinnamon, or cocoa greasepaint. These complements can provide agreeableness and flavor without the adverse effects on glucose.
Milk Choices and Glucose situations
The type of milk added to coffee can impact its impact on blood sugar. Whole milk is preferable over oat milk or skim milk because it contains more protein and fat, which help stabilize glucose situations. Thin nut milks, such as almond, pistachio, and coconut milk, are also excellent choices as they generally have lower glucose levels compared to grain-ground milks like oat or rice milk. Whole milk is better than skim milk because the fat content in whole milk slows down the immersion of sugar, leading to a lower glucose shaft.
Conclusion
Coffee, when consumed courteously, can be a healthy part of your diet with several benefits, including a reduced threat of type 2 diabetes. By understanding how coffee interacts with glucose situations and making informed choices about timing and complements, you can maximize its health benefits while minimizing implicit downsides. So, enjoy your coffee, but do it wisely to insure it supports your overall health.











+ There are no comments
Add yours